The benefits of iris identification
Iris recognition has been used in commercial applications since 1995, and is continually advancing with ever better algorithms and hardware. It was initially introduced as an identification system for government applications, typically in policing and justice, but has grown rapidly and, today, is used for many applications and mobile devices.
Iris Identification
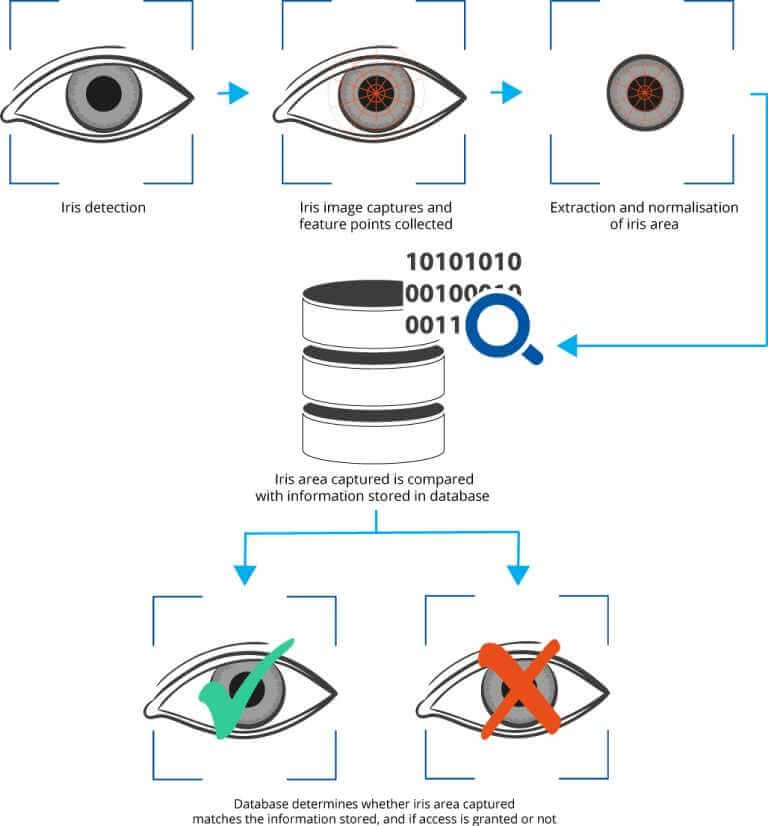
The human iris, the coloured part of the eye, is a muscle that is responsible for how much light reaches the retina. Each person’s iris is unique with a pattern formed of features known as corona, crypts, filaments, freckles, pits, furrows, striations and rings. Iris scanning methods can typically capture and detect around 200 distinct features.
Image capture
Using an infrared lamp to light the iris, scanning devices take a high -resolution image of the eye and then match the unique pattern of iris features against those stored in the biometric database. The database itself does not store images of the iris, but rather encoded features which are matched to the real-time scan, this is known as the biometric template.
Image optimisation
The image capture and optimisation process are key – the system needs a clear, focused image to define the iris boundaries and then extract the features for analysis and matching against the database.
Image matching
Once the system has identified the area to be extracted, an optimisation process takes place to eliminate shadowing, areas covered by the eyelid and any reflective areas. The final image is put into a rectangular block to provide static dimensions that can be used to match it against the biometric template.
Business applications
Iris recognition systems are often combined with other modalities in a multi-modal identification system for greater security. This modality is easily scaled for any size organisation or user environment.
Industry solutions
The increasing sophistication of iris recognition systems makes them ideal for high value, high-security environments, with large numbers of enrolments.
Benefits summary
High accuracy
The use of a 512-byte encoded biometric template means that creating a fake match or spoof is virtually impossible.
Contactless
Iris recognition is non-invasive and non-contact. The user simply looks at a camera and the process occurs automatically.
High scalability
Iris recognition systems are well-suited to business and applications with a large number of users. It is the only biometric technology that works in the 1:n or exhaustive search mode, meaning it can continually process users without downtime.
Let’s start a conversation
Deciding which biometric modality to use can be confusing. But remember, the technology is only a small part of a successful solution. We focus on your business challenges first, to determine what solution will work best for your environment. In fact, that’s why Argus exists. We’d love to help you put identity at the centre of your organisation, so let’s connect!





